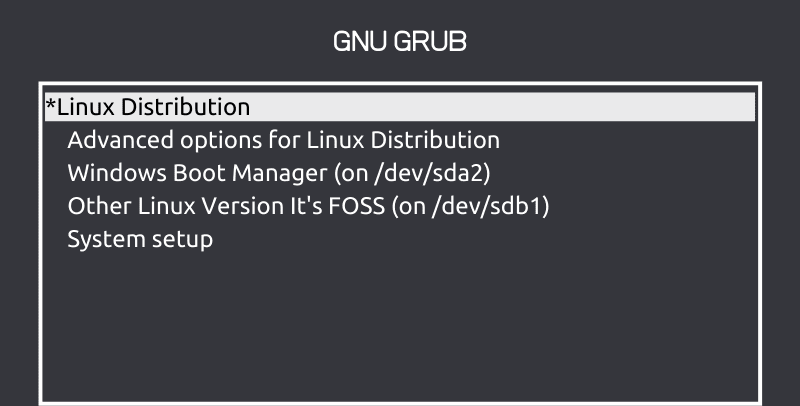
What is Grub in Linux? What is it used for? – If you ever used a desktop Linux system, you must have seen this screen. This is called the GRUB screen. Yes, it is written in all capital letters.
What is GRUB?
GRUB is a complete program for loading and managing the boot process. It is the most common bootloader for Linux distributions. A bootloader is the first software that runs when a computer starts. It loads the kernel of the operating system and then the kernel initializes the rest of the operating system: shell, display manager, desktop environment, etc.
Boot loader vs boot manager
I didn’t want to confuse you at this stage but this topic needs to be introduced before going on. There is a blurry line between a bootloader and a boot manager.
You already know that the bootloader starts first and then loads the kernel into memory and executes it. A boot manager program allows you to choose between operating systems if there is more than one on your system. A boot manager doesn’t load the OS directly,
With Linux kernel version 3.3, the Linux kernel includes a built-in EFI bootloader. In fact, any operating system that is capable of working the EFI system includes an EFI bootloader. In EFI capable systems, the firmware reads the EFI system partition (ESP) to locate the EFI files for boot information.
GRUB is both a bootloader and a boot manager. I’ll come back to GRUB in a moment. First, let’s see other GRUB-like programs.
[box type=”info” align=”aligncenter” class=”” width=””]GRUB is acronym for GRand Unified Bootloader.[/box]
What are some other boot managing programs similar to GRUB?
GRUB is the most popular boot manager for Linux. But it is not the only one. There is the highly customizable rEFInd boot manager that some Linux users love.
There is also systemd-boot text-based boot manager. You can guess that this is exclusively for systemd-based Linux distributions. Some distributions such as Pop OS, use the systemd-boot.
Accessing or editing GRUB
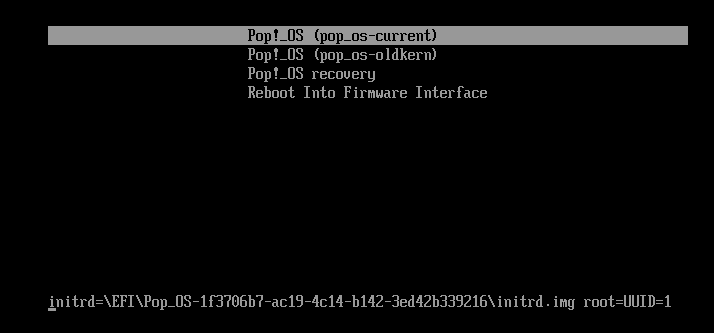
The usual GRUB screen you see is its menu interface. It allows you to choose which operating systems to boot, if there is more than one on your machine. You can also choose to load a different kernel if your Linux distribution as more than one installed.
Depending upon the configuration set by the Linux distribution, you may have some other entries on the GRUB menu.
You can edit a GRUB menu entry by pressing the “e” key. This way, you can change the kernel parameters before loading it. For example, in some cases, disabling the graphics driver from the kernel helps you with Linux system stuck at boot.
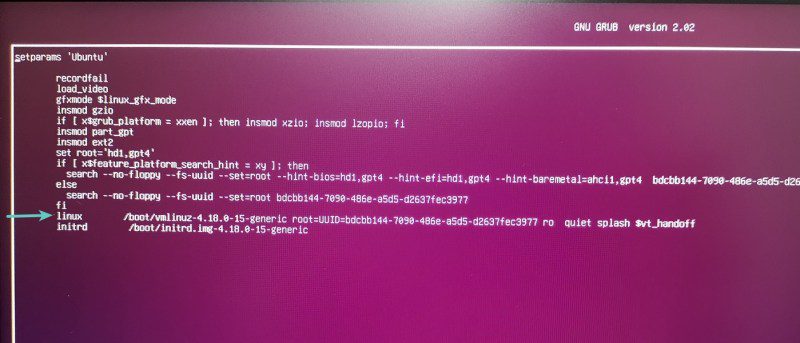
You can also enter the command line menu of GRUB using the “c” key at the GRUB menu interface.
GRUB configuration file
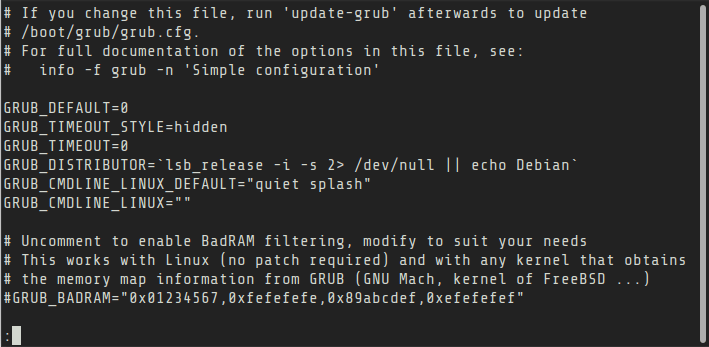
Any changes you make to GRUB from the menu interface is temporary. If you want to make some permanent changes to GRUB, such as changing the default timeout, you can change the configuration file after you boot into your Linux system.
The default GRUB configuration file is located at /etc/default/grub. There is also a /etc/default/grub.d directory. You may edit the /etc/default/grub file directly, however it is advised to make additional changes by adding config files (.cfg files) in this directory.
You must update GRUB for the changes to take into effect. In fact, whenever you install an additional Linux on your system, it will try to overwrite the existing GRUB config with its own.
GRUB customizer for easily customizing GRUB
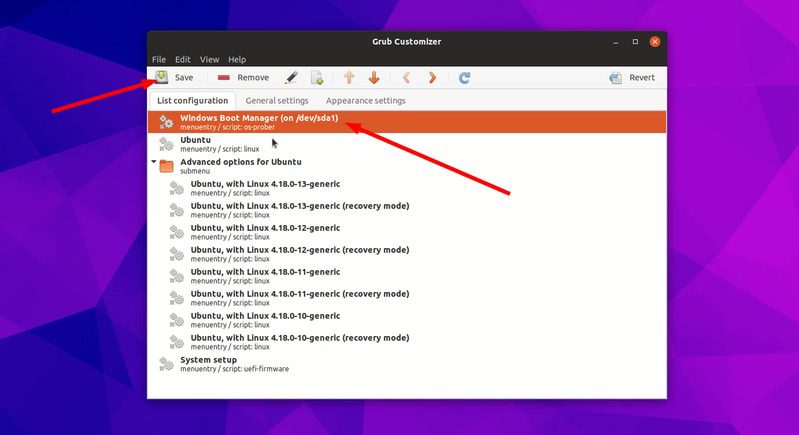
If you think editing a file with a text editor in the terminal is not something you feel comfortable with, you can use a graphical tool called GRUB Customizer.
It allows you to change the boot order, default timeout etc. You can also use it to change the background of GRUB with custom wallpaper.
GRUB Customizer can be installed in Ubuntu 20.04 from the Universe repository and via PPA in Ubuntu 18.04. It is available via AUR in Arch Linux based distributions.