SQL is a language to operate databases; it includes database creation, deletion, fetching rows, modifying rows, etc. SQL is an ANSI (American National Standards Institute) standard language, but there are many different versions of the SQL language.
What is SQL?
SQL is Structured Query Language, which is a computer language for storing, manipulating and retrieving data stored in a relational database.
SQL is the standard language for Relational Database System. All the Relational Database Management Systems (RDMS) like MySQL, MS Access, Oracle, Sybase, Informix, Postgres and SQL Server use SQL as their standard database language.
Also, they are using different dialects, such as −
- MS SQL Server using T-SQL,
- Oracle using PL/SQL,
- MS Access version of SQL is called JET SQL (native format) etc.
Why SQL?
SQL is widely popular because it offers the following advantages −
- Allows users to access data in the relational database management systems.
- Allows users to describe the data.
- Allows users to define the data in a database and manipulate that data.
- Allows to embed within other languages using SQL modules, libraries & pre-compilers.
- Allows users to create and drop databases and tables.
- Allows users to create view, stored procedure, functions in a database.
- Allows users to set permissions on tables, procedures and views.
A Brief History of SQL
- 1970 − Dr. Edgar F. “Ted” Codd of IBM is known as the father of relational databases. He described a relational model for databases.
- 1974 − Structured Query Language appeared.
- 1978 − IBM worked to develop Codd’s ideas and released a product named System/R.
- 1986 − IBM developed the first prototype of relational database and standardized by ANSI. The first relational database was released by Relational Software which later came to be known as Oracle.
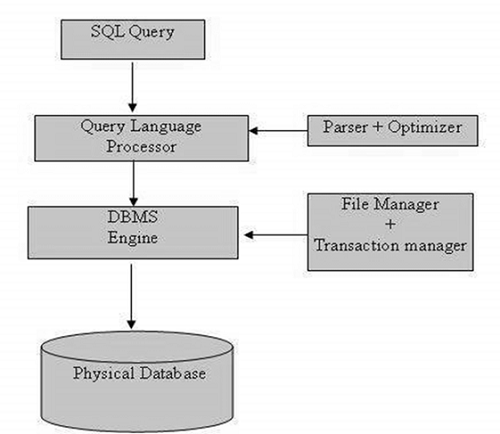
SQL Process
When you are executing an SQL command for any RDBMS, the system determines the best way to carry out your request and SQL engine figures out how to interpret the task.
There are various components included in this process.
These components are −
- Query Dispatcher
- Optimization Engines
- Classic Query Engine
- SQL Query Engine, etc.
A classic query engine handles all the non-SQL queries, but a SQL query engine won’t handle logical files.
Following is a simple diagram showing the SQL Architecture −
SQL Commands
The standard SQL commands to interact with relational databases are CREATE, SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE and DROP. These commands can be classified into the following groups based on their nature −
DDL – Data Definition Language
| Sr.No. | Command & Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | CREATE Creates a new table, a view of a table, or other object in the database. |
| 2 | ALTER Modifies an existing database object, such as a table. |
| 3 | DROP Deletes an entire table, a view of a table or other objects in the database. |
DML – Data Manipulation Language
| Sr.No. | Command & Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | SELECT Retrieves certain records from one or more tables. |
| 2 | INSERT Creates a record. |
| 3 | UPDATE Modifies records. |
| 4 | DELETE Deletes records. |
DCL – Data Control Language
| Sr.No. | Command & Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | GRANT Gives a privilege to user. |
| 2 | REVOKE Takes back privileges granted from user. |