Pandas library in the Python programming language is widely used for its ability to create various kinds of data structures and it also offers many operations to be performed on numeric and time-series data. By displaying a panda dataframe in Heatmap style, the user gets a visualisation of the numeric data. It gives an overview of the complete dataframe which makes it very much easy to understand the key points in the dataframe.
A heatmap is a matrix kind of 2-dimensional figure which gives a visualisation of numerical data in the form of cells. Each cell of the heatmap is coloured and the shades of colour represent some kind of relationship of the value with the dataframe. Following are some ways to display a Panda dataframe in Heatmap style.
Consider this DataFrame as an example:
Method 1 : By Using Pandas Library
In this method, the Pandas library will be used to generate a dataframe and the heatmap for it. The cells of the heatmap will display values corresponding to the dataframe. Below is the implementation.
# Python program to generate a heatmap
# which displays the value in each cell
# corresponding to the given dataframe
# import required libraries
import pandas as pd
# defining index for the dataframe
idx = ['1', '2', '3', '4']
# defining columns for the dataframe
cols = list('ABCD')
# entering values in the index and columns
# and converting them into a panda dataframe
df = pd.DataFrame([[10, 20, 30, 40], [50, 30, 8, 15],
[25, 14, 41, 8], [7, 14, 21, 28]],
columns = cols, index = idx)
# displaying dataframe as an heatmap
# with diverging colourmap as virdis
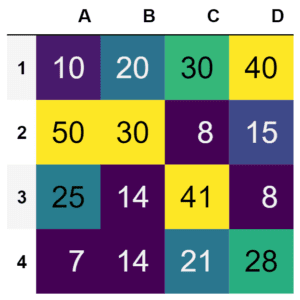
df.style.background_gradient(cmap ='viridis')\
.set_properties(**{'font-size': '20px'})Output :
Method 2 : By Using Matplotlib Library
In this method, the Panda dataframe will be displayed as a heatmap where the cells of the heatmap will be colour-coded according to the values in the dataframe. A colour bar will be present besides the heatmap which acts as a legend for the figure. Below is the implementation.
# Python program to generate a heatmap
# which represents panda dataframe
# in colour coding schemes
# import required libraries
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
# Defining index for the dataframe
idx = ['1', '2', '3', '4']
# Defining columns for the dataframe
cols = list('ABCD')
# Entering values in the index and columns
# and converting them into a panda dataframe
df = pd.DataFrame([[10, 20, 30, 40], [50, 30, 8, 15],
[25, 14, 41, 8], [7, 14, 21, 28]],
columns = cols, index = idx)
# Displaying dataframe as an heatmap
# with diverging colourmap as RdYlBu
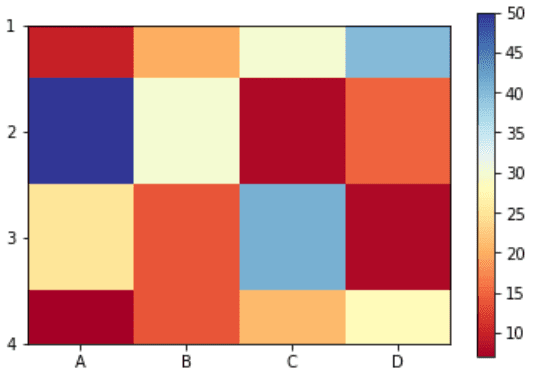
plt.imshow(df, cmap ="RdYlBu")
# Displaying a color bar to understand
# which color represents which range of data
plt.colorbar()
# Assigning labels of x-axis
# according to dataframe
plt.xticks(range(len(df)), df.columns)
# Assigning labels of y-axis
# according to dataframe
plt.yticks(range(len(df)), df.index)
# Displaying the figure
plt.show()Output :
Method 3 : By Using Seaborn Library
In this method, a heatmap will be generated out of a Panda dataframe in which cells of the heatmap will contain values corresponding to the dataframe and will be color-coded. A color bar will also present besides the heatmap which acts as a legend for the figure. Below is the implementation.
# Python program to generate heatmap which
# represents panda dataframe in color-coding schemes
# along with values mentioned in each cell
# import required libraries
import pandas as pd
import seaborn as sns % matplotlib inline
# Defining figure size
# for the output plot
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize = (12, 7))
# Defining index for the dataframe
idx = ['1', '2', '3', '4']
# Defining columns for the dataframe
cols = list('ABCD')
# Entering values in the index and columns
# and converting them into a panda dataframe
df = pd.DataFrame([[10, 20, 30, 40], [50, 30, 8, 15],
[25, 14, 41, 8], [7, 14, 21, 28]],
columns = cols, index = idx)
# Displaying dataframe as an heatmap
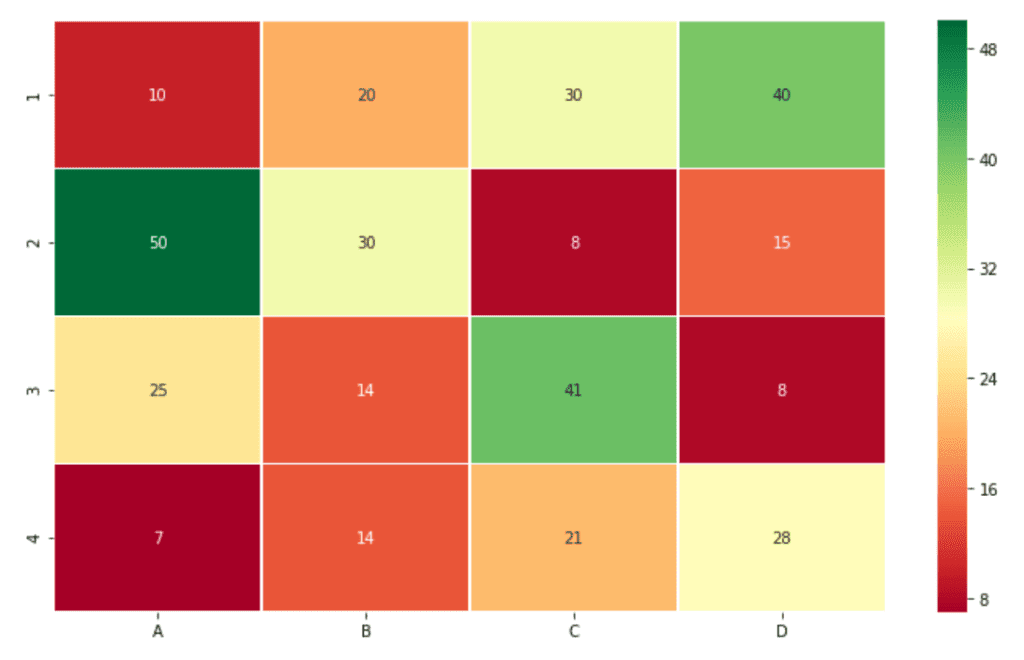
# with diverging colourmap as RdYlGn
sns.heatmap(df, cmap ='RdYlGn', linewidths = 0.30, annot = True)Output :
If the uppermost and the lowermost row of output figure does not appear with proper height then add below two lines after the last line of the above code.
bottom, top = ax.get_ylim()
ax.set_ylim(bottom + 0.5, top - 0.5)Method 4: Generating Correlation Matrix Using Panda Library
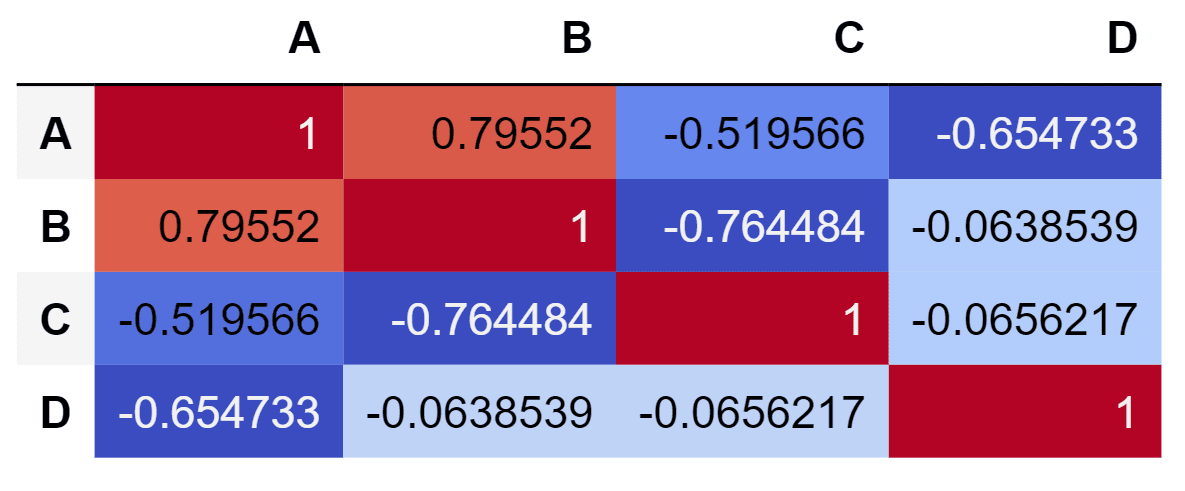
A correlation matrix is a special kind of heatmap which display some insights of the dataframe. The cells of this heatmap display the correlation coefficients which is the linear historical relationship between the variables of the dataframe. In this method only Pandas library is used to generate the correlation matrix. Below is the implementation.
# Python program to generate heatmap
# which represents correlation between
# columns of panda dataframe
# import required libraries
import pandas as pd
# Defining index for the dataframe
idx = ['1', '2', '3', '4']
# Defining columns for the dataframe
cols = list('ABCD')
# Entering values in the index and columns
# and converting them into a panda dataframe
df = pd.DataFrame([[10, 20, 30, 40], [50, 30, 8, 15],
[25, 14, 41, 8], [7, 14, 21, 28]],
columns = cols, index = idx)
# generating pairwise correlation
corr = df.corr()
# Displaying dataframe as an heatmap
# with diverging colourmap as coolwarm
corr.style.background_gradient(cmap ='coolwarm')Output :
Method 5: Generating Correlation Matrix Using Seaborn Library
The correlation matrix can also be generated using Seaborn library. The cells of the generated heatmap will contain the correlation coefficients but the values are round off unlike heatmap generated by Pandas library. Below is the implementation.
# Python program to generate a heatmap
# which represents the correlation between
# columns of panda dataframe
# import required libraries
import pandas as pd
import seaborn as sn
# Defining figure size
# for the output plot
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize = (12, 7))
# Defining index for the dataframe
idx = ['1', '2', '3', '4']
# Defining columns for the dataframe
cols = list('ABCD')
# Entering values in the index and columns
# and converting them into a panda dataframe
df = pd.DataFrame([[10, 20, 30, 40], [50, 30, 8, 15],
[25, 14, 41, 8], [7, 14, 21, 28]],
columns = cols, index = idx)
df = pd.DataFrame(df, columns =['A', 'B', 'C', 'D'])
corr = df.corr()
sn.heatmap(corr, annot = True)Output :
If the uppermost and the lowermost row of output figure does not appear with proper height then add below two lines after the last line of the above code.
bottom, top = ax.get_ylim()
ax.set_ylim(bottom + 0.5, top - 0.5)