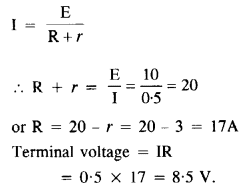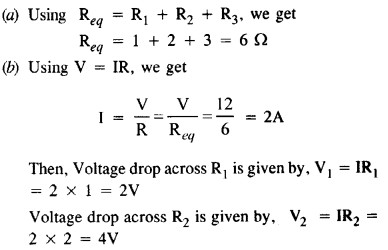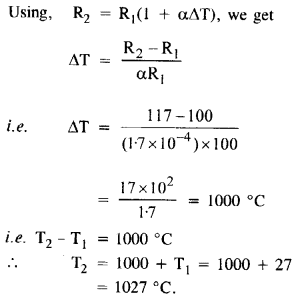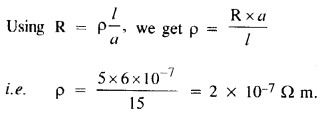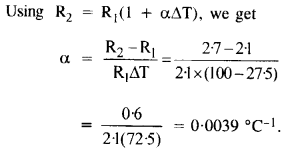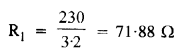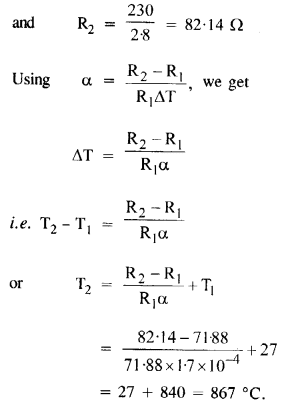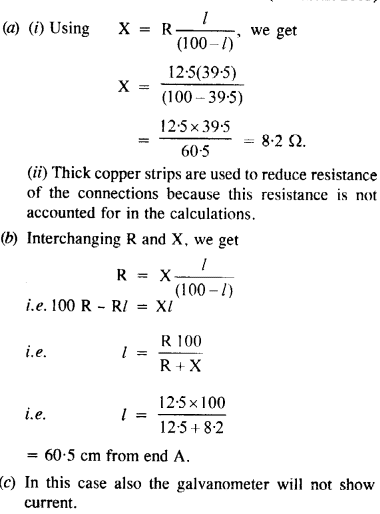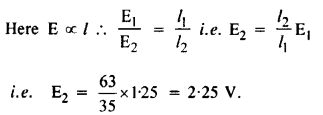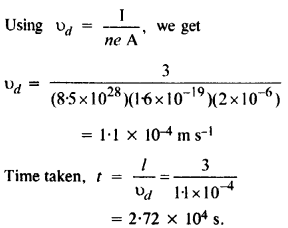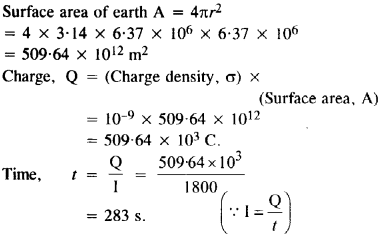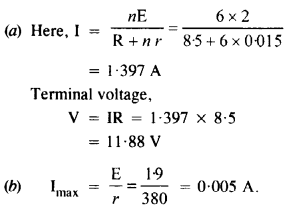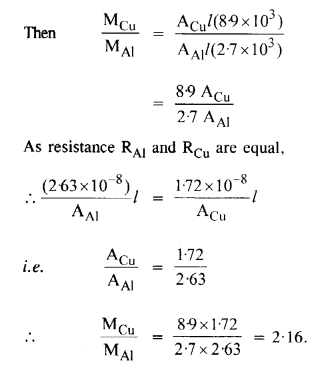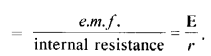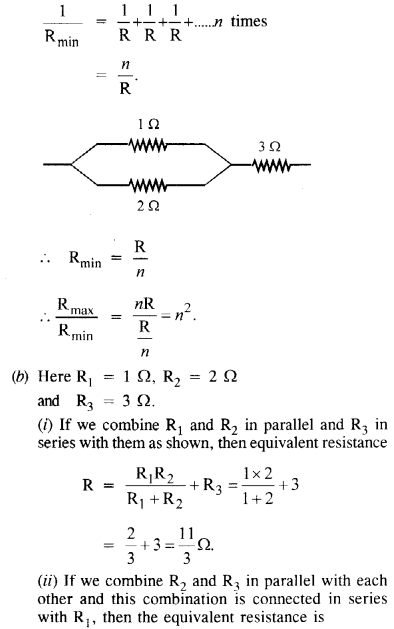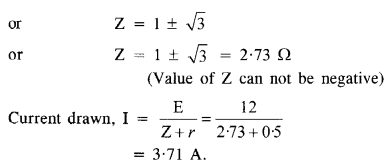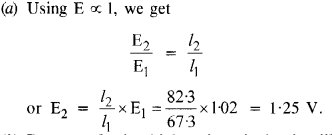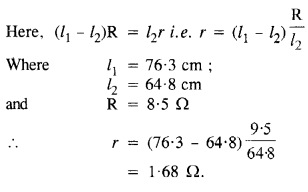Topics and Subtopics in NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 3 Current Electricity:
| Section Name | Topic Name |
| 3 | Current Electricity |
| 3.1 | Introduction |
| 3.2 | Electric Current |
| 3.3 | Electric Currents in Conductors |
| 3.4 | Ohm’s law |
| 3.5 | Drift of Electrons and the Origin of Resistivity |
| 3.6 | Limitations of Ohm’s Law |
| 3.7 | Resistivity of Various Materials |
| 3.8 | Temperature Dependence of Resistivity |
| 3.9 | Electrical Energy, Power |
| 3.10 | Combination of Resistors — Series and Parallel |
| 3.11 | Cells, emf, Internal Resistance |
| 3.12 | Cells in Series and in Parallel |
| 3.13 | Kirchhoff’s Rules |
| 3.14 | Wheatstone Bridge |
| 3.15 | Meter Bridge |
| 3.16 | Potentiometer |
Question 1.
The storage battery of a car has an e.m.f. of 12 V. If the internal resistance of the battery is 0.4Ω, what is the maximum current that can be drawn from the battery ?
Answer:
Question 2.
A battery of e.m.f. 10 V and internal resistance 3Ω is connected to a resistor. If the current in the circuit is 0.5 A, what is the resistance of the resistor ? What is the terminal voltage of the battery when the circuit is closed ?
Answer:
Question 3.
(a) Three resistors IΩ, 2 Ωand 3 Ω are combined in series. What is the total resistance of the combination ?
(b) If the combination is connected to a battery of e.m.f. 12 V and negligible internal resistance, obtain the potential drop across each resistor.
Answer:
Voltage drop across R3 is given by, V3 = IR3 = 2 x 3 = 6V.
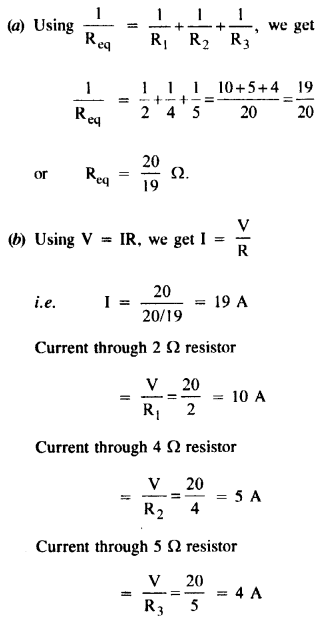
Question 4.
(a) Three resistors 2 Ω, 4 Ω, and 5 Ω, are combined in parallel. What is the total resistance of the combination ?
(b) If the combination is connected to a battery of e.m.f. 20 V and negligible internal resistance, determine the current through each resistor, and the total current drawn from the battery.
Answer:
Question 5.
At room temperature (27.0 °C) the resistance of a heating element is 100 Ω. What is the temperature of the element if the resistance is found to be 117 Ω, given that the temperature coefficient of the material of the resistor is 1.70 x 10-4 °C-1.
Answer:
Question 6.
A negligibly small current is passed through a wire of length 15 m and uniform cross-section 6.0 x 10-7 m2, and its resistance is measured to be 50 Ω. What is the resistivity of the material at the temperature of the experiment ?
Answer:
Question 7.
A silver wire has a resistance of 2.1 Ω at 27.5 °C, and a resistance of 2.7 Ω at 100 °C. Determine the temperature co-efficient of resistivity of silver.
Answer:
Question 8.
A heating element using nichrome connected to a 230 V supply draws an initial current of 3.2 A which settles after a few seconds to a steady value of 2.8 A. What is the steady temperature of the heating element if the room temperature is 27.0 °C ? Temperature coefficient of resistance of nichrome averages over the temperature range involved is 1.70 X 10-4 °C-1.
Answer:
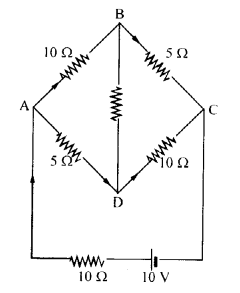
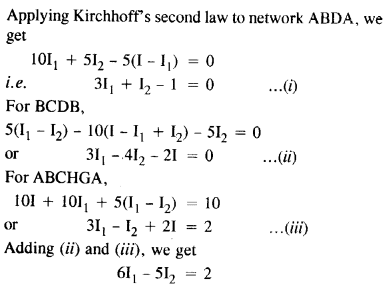
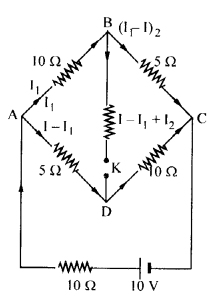
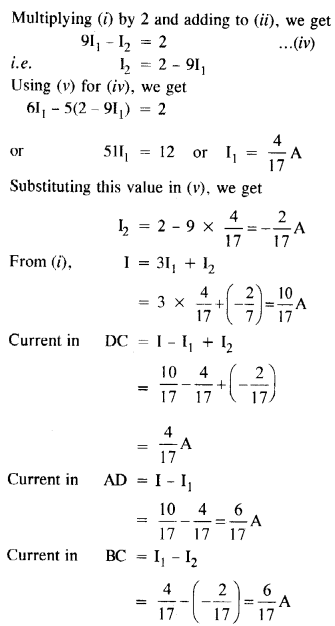
Question 9.
Determine the current in each branch of the network shown in Figure
Answer:
Question 10.
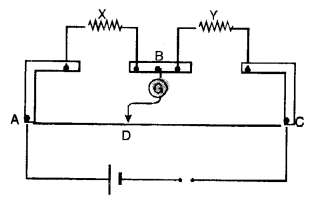
(a) In a meter bridge (Figure), the balance point is found to be at 39.5 cm from the end A, when the resistor Y is of 12.5 Ω. Determine the resistance of X. Why are the connections between resistors in a Wheatstone or meter bridge made of thick copper strips ?
(b) Determine the balance point of the bridge above if X and Y are interchanged.
(c) What happens if the galvanometer and cell are interchanged at the balance point of the bridge ? Would the galvanometer show any current ? (C.B.S.E. 2005)
Answer:
Question 11.
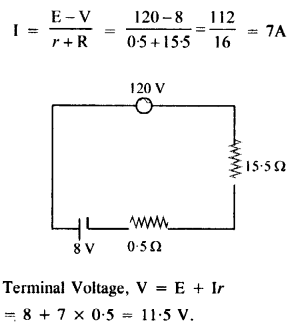
A storage battery of e.m.f. 8.0 V and internal resistance 0.5 Ω is being charged by a 120 V dc supply using a series resistor of 15.5 Ω. What is the terminal voltage of the battery during charging ? What is the purpose of having a series resistor in the charging circuit ?
Answer:
During charging,
V = E + I(r + R)
Question 12.
In a potentiometer arrangement, a cell of e.m.f. 1.25 V gives a balance point at 35.0 cm length of the wire. If the cell is replaced by another cell and the balance point shifts to 63.0 cm, what is the e.m.f. of the second cell ?
Answer:
Question 13.
The number density of free electrons in a copper conductor estimated in Example 3.1 is 8.5 x 1028 m3. How long does an electron take to drift from one end of a wire 3.0 m long to its other end ? The area of crosssection of the wire is 2.0 x 10-6 m2 and it is carrying a current of 3.0 A.
Answer:
Question 14.
The earth’s surface has a negative surface charge density of 10-9 cm-2. The potential difference of 400 kV between the top of the atmosphere and the surface results (due to the low conductivity of the lower atmosphere) in a current of only 1800 A over the entire globe. If there were no mechanism of sustaining atmospheric electric Held, how much time (roughly) would be required to neutralise the earth’s surface ? (This never happens in practice because there is a mechanism to replenish electric charges, namely the continual thunderstorms and lightning in different parts of the globe.)
(Radius of earth = 6.37 x 106 m.)
Answer:
Question 15.
(a) Six lead-acid type of secondary cells each of e.m.f. 2.0 V and internal resistance 0.015 Ω are joined in series to provide a supply to a resistance of 8.5 Ω. What are the current drawn from the supply and its terminal voltage ?
(b) A secondary cell after long use has an e.m.f. of 1.9 V and a large internal resistance of 380 Ω. What maximum current can be drawn from the cell ? Could the cell drive the starting motor of a car ?
Answer:
It cannot be used for starting motor of a car because large current is needed to start the car.
Question 16.
Two wires of equal length, one of aluminium and the other of copper have the same resistance. Which of the two wires is lighter ? Hence explain why aluminium wires are preferred for overhead power cables. (PAL = 2.63 x 108 Ω m, Pcu= 1.72 X 1(H Ω m. Relative density of A1 = 2.7, of Cu = 8.9.)
Answer:
Aluminium is lighter, so it is used for overhead power cables.
Question 17.
What conclusion can you draw from the following observations on a resistor made of alloy manganin ?
| Current | Voltage | Current | Voltage |
| A | V | A | V |
| 0.2 | 3.94 | 3.0 | 59.2 |
| 0.4 | 78.7 | 4.0 | 78.8 |
| 0.6 | 11.8 | 5.0 | 98.6 |
| 0.8 | 15.7 | 6.0 | 118.5 |
| 1.0 | 19.7 | 7.0 | 138.2 |
| 2.0 | 39.4 | 8.0 | 158.0 |
Answer:
It indicates that Ohm’s law i.e.V α I is valid for a wide range.
Resistivity of Manganin remains nearly same with change in temperature.
Question 18.
Answer the following questions :
(a) A steady current flows in a metallic conductor of non-uniform cross-section. Which of these quantities is constant along the conductor : current, current density, electric field, drift speed ?
(b) Is Ohm’s law universally applicable for all conducting elements ? If not, give examples of elements which do not obey Ohm’s law.
(c) A low voltage supply from which one needs high currents must have very low internal resistance. Why?
(d) A high tension (HT) supply of, say, 6 kV must have a very large internal resistance. Why ?
Answer:
(a) Current, as it given to be steady.The other quantities depend inversely upon area of cross-section.
(b) Ohm’s law is not valid for electrolytes and semi-conductor diodes.
(c) Maximum current drawn
Clearly low r will ensure high current
(d) If internal resistance is not large, then the heavy current drawn during accidental short circuit can damage the supply.
Question 19.
Choose the correct alternative :
(a) Alloys of metals usually have (greater/less) resistivity than that of their constituent metals.
(b) Alloys usually have much (lower/higher) temperature co-efficients of resistance than pure metals.
(c) The resistivity of the alloy manganin is nearly independent of/increases rapidly with increase of temperature.
(d) The resistivity of a typical insulator (e.g., amber) is greater than that of a metal by a factor of the order of (1022/10)3).
Answer:
(a) Greater
(b) Lower
(c) Nearly independent
(d)1022
Question 20.
(a) Given n resistors each of resistance R, how will you combine them to get the
(i) maximum (ii) minimum effective resistance ? What is the ratio of the maximum to minimum resistance ?
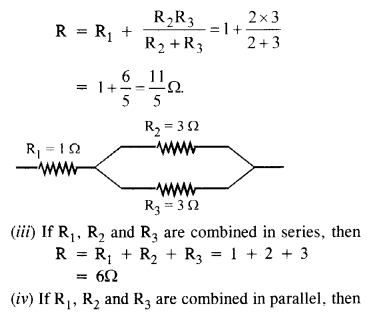
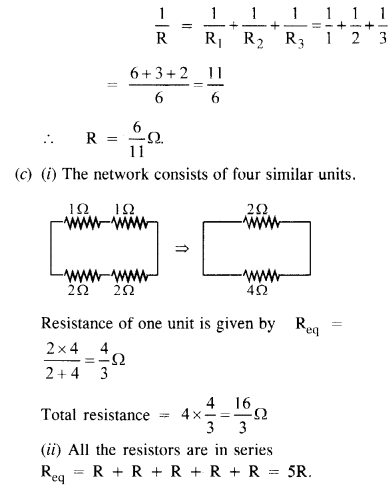
(b) Given the resistances of 1 Q, 2 G, 3 Q, how will be combine them to get an equivalent resistance of (i) (11/3)Ω (ii) (11/5) Ω, (iii) 6 Ω, (iv) (6/11) Ω ?
(c) Determine the equivalent resistance of networks shown in figure. (N.C,E.R,T.)
Answer:
(i) Maximum resistance can be obtained by combining them in series with each other.
The maximum resistance Rmax = R + R + R + ……………..n times = nR.
(ii) Minimum effective resistance can be obtained by combining them in parallel with each other. Minimum resistance Rmax is found as
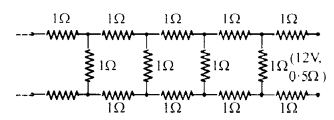
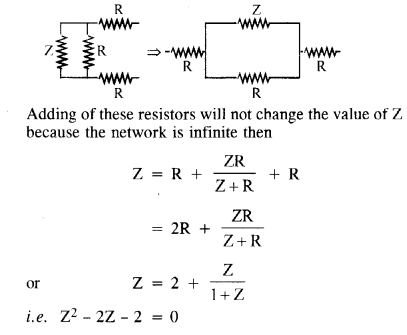
Question 21.
Determine the current drawn from a 12 V supply with internal resistance 0.5Ω by the infinite network shown in figure. Each resistor has 1 Ω resistance.(N.C.E.R.T.)
Answer:
Let the total resistance of the circuit be Z and a set of three resistors of value R each be connected to it as shown in the figure.
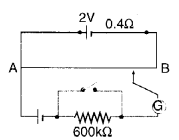
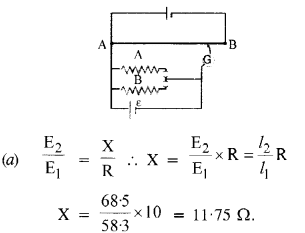
Question 22.
Figure shows a potentiometer with a cell of 2.0 V and internal resistance 0.40 Ω maintaining a potential drop across the resistor wire AB. A standard cell which maintains a constant e.m.f. of 1.02 V (for very moderate currents up to a few mA) gives a balance point at 67.3 cm length of the wire. To ensure very low currents drawn from the standard cell, a very high resistance of 600 kΩ is put in series with it, which is shorted close to the balance point. The standard cell is then replaced by a cell of unknown e.m.f. e and the balance point found similarly, turns out to be at 82.3 cm length of the wire.
(a) What is the value e ?
(b) What purpose does the high resistance of 600 kΩ have ?
(c) Is the balance point affected by this high resistance?
(d) Is the balance point affected by the internal resistance of the driver cell ?
(e) Would the method work in the above situation if the driver cell of the potentiometer had an e.m.f. of 1.0 V instead of 2.0 V ?
(f) Would the circuit work cell for determining an extremely small e.m.f., say of the order of a few mV (such as the typical e.m.f. of a thermo couple not, how will you modify the circuit?
Answer:
(b) Purpose of using high resistor is that it will allow very small current to flow through the galvanometer when the circuit is not balanced.
(c) No, the balance point is not affected by the high resistance.
(d) No, the balance point is not affected by the internal resistance of the driver cell.
(e) No, the method will not work in this situation because the balance point is not obtained if driver cell of e.m.f. 1V instead of 2V is used.
(f) The circuit will not work well for determining extremely small e.m.f. because in such cases the balance point will be almost on end A.
Question 23.
Figure shows a potentiometer circuit for comparison of two resistances. The balance point with a standard resistor R = 10.0 Ω is found to be 58.3 cm, while that with the unknown resistance X is 68.5 cm. Determine the value of X. What might you do if you failed to find a balance point with the given cell of emf ε ?
Answer:
(b) To obtain balance point, either a cell of less e.m.f. be used or a suitable resistor be put in series with R and X so that potential drop across the wire AB is reduced.
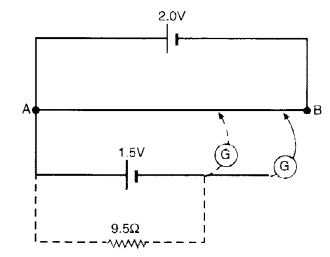
Question 24.
Figure shows a 2.0 V potentiometer used for the determination of internal resistance
1.5 V cell. The balance point of the cell in open circuit is 76.3 cm. When a resistor of
9.5 Ω is used in the external circuit of the cell, the balance point shifts to 64.8 cm length of the potentiometer wire. Determine the internal resistance of the cell.
Answer: