What is SAML?
- SAML stands for Security Assertion Markup language.
- Generally, users need to enter a username and password to login in any application.
- SAML is a technique of achieving Single Sign-On (SSO).
- Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) is an XML-based framework that allows the identity providers to provide the authorization credentials to the service provider.
- With SAML, you need to enter one security attribute to log in to the application
- SAML is a link between the authentication of the user’s identity and authorization to use a service.
- SAML provides a service known as Single Sign-On means that users have to log in once and can use the same credentials to log in to another service provider.
Why SAML?
- With SAML, both the service provider and identity provider exist separately, but centralizes the user management and provides access to the SaaS solutions.
- SAML authentication is mainly used for verifying the user’s credentials from the identity provider.
Advantages of SAML:
- SAML SSO (SINGLE SIGN-ON): SAML provides security by eliminating passwords for an app and replacing them with the security tokens. Since we do not require any passwords for SAML logins, there is no risk of credentials to be stolen by unauthorized users. It provides faster, easier and trusted access to cloud applications.
- Open Standard SINGLE SIGN-ON: SAML implementations confirms to the open standard. Therefore, it is not restricted to a single identity provider. This open standard allows you to choose the SAML provider.
- Strong Security: SAML uses federated identities and secure tokens to make SAML one of the best secure forms for web-based authentication.
- Improved online experience for end users: SAML provides SINGLE SIGN-ON (SSO) to authenticate at an identity provider, and the identity provider sends the authentication to the service provider without additional credentials.
- Reduced administrative costs for service providers: Using single authentication multiple times for multiple services can reduce the administrative costs for maintaining the account information.
- Risk transference: SAML has put the responsibility of handling the identities to the identity provider.
Types of SAML providers
SAML provider is an entity within a system that helps the user to access the services that he or she wants.
There are two types of SAML providers:
- Service provider
- Identity provider
Service provider
- It is an entity within a system that provides the services to the users for which they are authenticated.
- Service provider requires authentication from the identity provider that grants access to the user.
- Salesforce and other CRM are common service providers.
Identity provider
- An identity provider is an entity within a system that sends the authentication to the service provider is about who they are along with the user access rights.
- It maintains a directory of the user and provides an authentication mechanism.
- Microsoft Active Directory and Azure are common identity providers.
What is a SAML Assertion?
A SAML Assertion is an XML document that the identity provider sends to the service provider containing user authorization.
SAML Assertion is of three types:
- Authentication
- It proves the identification of the user
- It provides the time at which the user logged in.
- It also determines which method of authentication has been used.
- Attribute
- An attribute assertion is used to pass the SAML attributes to the service provider where attribute contains a piece of data about the user authentication.
- Authorization decision
- An authorization decision determines whether the user is authorized to use the service or identity provider denied the request due to the password failure.
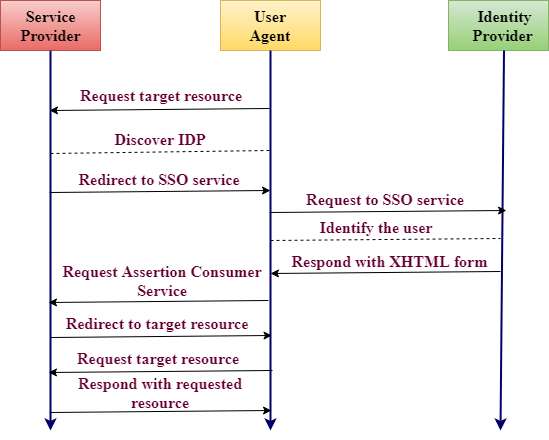
Working of SAML
- If a user tries to access the resource on the server, the service provider checks whether the user is authenticated within the system or not. If you are, you skip to step 7, and if you are not, the service provider starts the authentication process.
- The service provider determines the appropriate identity provider for you and redirects the request to the identity provider.
- An authentication request has been sent to the SSO (SINGLE SIGN-ON) service, and SSO service identifies you.
- The SSO service returns with an XHTML document, which contains authentic information required by the service provider in a SAMLResponse parameter.
- The SAMLResponse parameter is passed to the Assertion Consumer Service (ACS) at the service provider.
- The service provider processes the request and creates a security context; you automatically logged in.
- After login, you can request for a resource that you want.
- Finally, the resource is returned to you.