Amazon Web Services – Basic Architecture
This is the basic structure of AWS EC2, where EC2 stands for Elastic Compute Cloud. EC2 allow users to use virtual machines of different configurations as per their requirement. It allows various configuration options, mapping of individual server, various pricing options, etc. We will discuss these in detail in AWS Products section. Following is the diagrammatic representation of the architecture.
Note − In the above diagram S3 stands for Simple Storage Service. It allows the users to store and retrieve various types of data using API calls. It doesn’t contain any computing element. We will discuss this topic in detail in AWS products section.
Load Balancing
Load balancing simply means to hardware or software load over web servers, that improver’s the efficiency of the server as well as the application. Following is the diagrammatic representation of AWS architecture with load balancing.
The hardware load balancer is a very common network appliance used in traditional web application architectures.
AWS provides the Elastic Load Balancing service, it distributes the traffic to EC2 instances across multiple available sources, and dynamic addition and removal of Amazon EC2 hosts from the load-balancing rotation.
Elastic Load Balancing can dynamically grow and shrink the load-balancing capacity to adjust to traffic demands and also support sticky sessions to address more advanced routing needs.
Amazon Cloud-front
It is responsible for content delivery, i.e. used to deliver website. It may contain dynamic, static, and streaming content using a global network of edge locations. Requests for content at the user’s end are automatically routed to the nearest edge location, which improves the performance.
Amazon Cloud-front is optimized to work with other Amazon Web Services, like Amazon S3 and Amazon EC2. It also works fine with any non-AWS origin server and stores the original files in a similar manner.
In Amazon Web Services, there are no contracts or monthly commitments. We pay only for as much or as little content as we deliver through the service.
Elastic Load Balancer
It is used to spread the traffic to web servers, which improves performance. AWS provides the Elastic Load Balancing service, in which traffic is distributed to EC2 instances over multiple available zones, and dynamic addition and removal of Amazon EC2 hosts from the load-balancing rotation.
Elastic Load Balancing can dynamically grow and shrink the load-balancing capacity as per the traffic conditions.
Security Management
Amazon’s Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) provides a feature called security groups, which is similar to an inbound network firewall, in which we have to specify the protocols, ports, and source IP ranges that are allowed to reach your EC2 instances.
Each EC2 instance can be assigned one or more security groups, each of which routes the appropriate traffic to each instance. Security groups can be configured using specific subnets or IP addresses which limits access to EC2 instances.
Elastic Caches
Amazon Elastic Cache is a web service that manages the memory cache in the cloud. In memory management, cache has a very important role and helps to reduce the load on the services, improves the performance and scalability on the database tier by caching frequently used information.
Amazon RDS
Amazon RDS (Relational Database Service) provides a similar access as that of MySQL, Oracle, or Microsoft SQL Server database engine. The same queries, applications, and tools can be used with Amazon RDS.
It automatically patches the database software and manages backups as per the user’s instruction. It also supports point-in-time recovery. There are no up-front investments required, and we pay only for the resources we use.
Hosting RDMS on EC2 Instances
Amazon RDS allows users to install RDBMS (Relational Database Management System) of your choice like MySQL, Oracle, SQL Server, DB2, etc. on an EC2 instance and can manage as required.
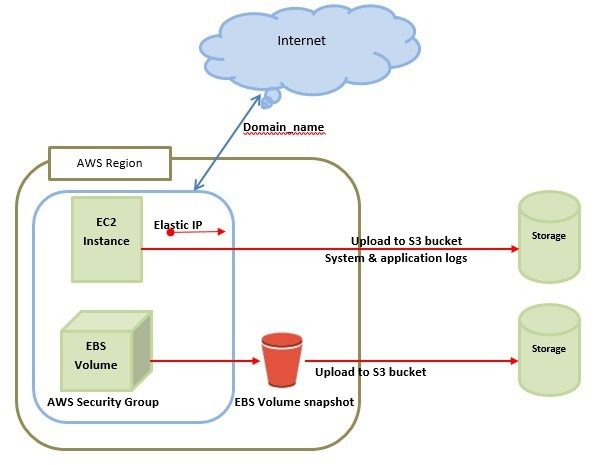
Amazon EC2 uses Amazon EBS (Elastic Block Storage) similar to network-attached storage. All data and logs running on EC2 instances should be placed on Amazon EBS volumes, which will be available even if the database host fails.
Amazon EBS volumes automatically provide redundancy within the availability zone, which increases the availability of simple disks. Further if the volume is not sufficient for our databases needs, volume can be added to increase the performance for our database.
Using Amazon RDS, the service provider manages the storage and we only focus on managing the data.
Storage & Backups
AWS cloud provides various options for storing, accessing, and backing up web application data and assets. The Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service) provides a simple web-services interface that can be used to store and retrieve any amount of data, at any time, from anywhere on the web.
Amazon S3 stores data as objects within resources called buckets. The user can store as many objects as per requirement within the bucket, and can read, write and delete objects from the bucket.
Amazon EBS is effective for data that needs to be accessed as block storage and requires persistence beyond the life of the running instance, such as database partitions and application logs.
Amazon EBS volumes can be maximized up to 1 TB, and these volumes can be striped for larger volumes and increased performance. Provisioned IOPS volumes are designed to meet the needs of database workloads that are sensitive to storage performance and consistency.
Amazon EBS currently supports up to 1,000 IOPS per volume. We can stripe multiple volumes together to deliver thousands of IOPS per instance to an application.
Auto Scaling
The difference between AWS cloud architecture and the traditional hosting model is that AWS can dynamically scale the web application fleet on demand to handle changes in traffic.
In the traditional hosting model, traffic forecasting models are generally used to provision hosts ahead of projected traffic. In AWS, instances can be provisioned on the fly according to a set of triggers for scaling the fleet out and back in. Amazon Auto Scaling can create capacity groups of servers that can grow or shrink on demand.
Key Considerations for Web Hosting in AWS
Following are some of the key considerations for web hosting −
No physical network devices needed
In AWS, network devices like firewalls, routers, and load-balancers for AWS applications no longer reside on physical devices and are replaced with software solutions.
Multiple options are available to ensure quality software solutions. For load balancing choose Zeus, HAProxy, Nginx, Pound, etc. For establishing a VPN connection choose OpenVPN, OpenSwan, Vyatta, etc.
No security concerns
AWS provides a more secured model, in which every host is locked down. In Amazon EC2, security groups are designed for each type of host in the architecture, and a large variety of simple and tiered security models can be created to enable minimum access among hosts within your architecture as per requirement.
Availability of data centers
EC2 instances are easily available at most of the availability zones in AWS region and provides model for deploying your application across data centers for both high availability and reliability.